Understanding Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Kidney disease affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to a significant decline in kidney function, impacting overall health and well-being. For individuals with advanced kidney disease, dialysis becomes a crucial component of their treatment plan.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, two primary types of dialysis treatments. We will explore the differences between these modalities, their benefits, potential complications, and essential considerations for individuals considering or undergoing dialysis.
By gaining insights into these life-saving treatments, individuals and their loved ones can make informed decisions about managing kidney disease.
1. What Is Hemodialysis?
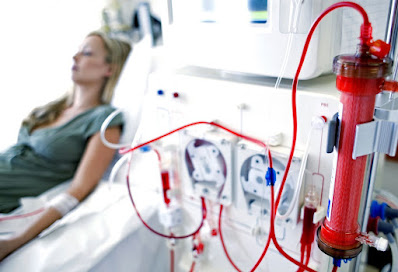
Hemodialysis is a process that involves removing waste products and excess fluids from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to perform this function effectively. During hemodialysis, the patient's blood is filtered through a dialyzer, a machine that acts as an artificial kidney.
This procedure typically takes place at a dialysis center, where patients receive treatment under the supervision of trained healthcare professionals.
Hemodialysis Process:
- The patient's blood is pumped out of their body and directed into the dialyzer.
- Within the dialyzer, the blood passes through a semipermeable membrane, allowing waste products and excess fluids to be removed.
- The purified blood is then returned to the patient's body.
Advantages of Hemodialysis:
- Efficient removal of waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
- Regular sessions allow for close monitoring of patients' health status.
- Suitable for patients who prefer receiving treatment at a medical facility.
Disadvantages of Hemodialysis:
- Requires adherence to a strict treatment schedule.
- Potential for vascular access-related complications, such as infection or blood clotting.
- Lifestyle adjustments may be necessary to accommodate dialysis sessions.
When exploring options for kidney disease management, it is essential to consider the merits of hemodialysis. Hemodialysis is known for its efficiency in eliminating waste products and maintaining fluid balance in the body. Additionally, the structured nature of hemodialysis sessions allows healthcare professionals to closely monitor patients' health status and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
However, it is important to acknowledge the potential drawbacks of hemodialysis, including the need for strict adherence to a treatment schedule, the possibility of complications related to vascular access, and the impact on patients' daily routines. By understanding these aspects, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating hemodialysis into their lives.
Suggested post: Understanding Hemodialysis: Risks And Preparing For Hemodialysis
2. An Overview of Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis offers an alternative to hemodialysis and involves the use of the body's peritoneal membrane as a natural filter for waste removal. This form of dialysis can be performed at home, providing patients with a greater level of independence and flexibility in managing their treatment regimen.
Peritoneal Dialysis Process:
- A sterile solution (dialysate) is introduced into the patient's abdomen through a catheter.
- The peritoneal membrane, which lines the abdominal cavity, serves as a filter, allowing waste products and excess fluids to pass into the dialysate.
- After a prescribed dwell time, the used dialysate is drained from the abdomen, carrying the accumulated waste products out of the body.
Advantages of Peritoneal Dialysis:
- Offers greater flexibility and independence, as it can be performed at home.
- Gentler impact on the cardiovascular system compared to hemodialysis.
- Reduced dietary restrictions due to continuous nature of peritoneal dialysis.
Disadvantages of Peritoneal Dialysis:
- Risk of peritonitis, an infection of the peritoneal membrane, if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
- Potential for complications related to the catheter, such as obstruction or leakage.
- Requires regular monitoring and meticulous attention to technique and hygiene.
For individuals seeking a more flexible approach to dialysis, peritoneal dialysis presents an attractive option. The ability to perform dialysis at home empowers patients to take charge of their treatment schedule while experiencing a gentler impact on their cardiovascular system.
Furthermore, the continuous nature of peritoneal dialysis allows for fewer dietary restrictions, offering individuals a greater sense of freedom in their dietary choices. However, it is crucial to recognize the importance of vigilant hygiene practices and meticulous attention to technique in order to minimize the risk of peritoneal membrane infection and catheter-related complications.
By weighing these factors, individuals can determine whether peritoneal dialysis aligns with their lifestyle and treatment preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis serve as vital lifelines for individuals with advanced kidney disease, providing them with the opportunity to manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life. Each dialysis modality comes with its own set of benefits and considerations, and by understanding the important differences between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, individuals can make informed decisions about the most suitable treatment option for their specific needs.
Whether opting for the structured environment of a dialysis center with hemodialysis or the flexibility of performing treatment at home with peritoneal dialysis, both modalities offer effective waste removal and fluid balance management.
It is essential to consult with a nephrologist and a registered dietitian specializing in kidney health to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes dietary modifications to support overall health and optimize the benefits of dialysis. Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment protocols, and open communication with healthcare professionals are crucial elements for successful and sustainable dialysis management.
Remember, this article provides an overview of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis and should not replace personalized medical advice. Make sure to consult with your healthcare team for a comprehensive evaluation of your condition and appropriate guidance regarding your treatment options.
Sources:
1. National Kidney Foundation: https://www.kidney.org/
2. Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/
3. American Kidney Fund: https://www.kidneyfund.org/
4. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
.jpg)


Comments
Post a Comment
Share your views