6 Symptoms of Kidney Stones & Risk Factors
Kidney stones are a very common occurrence. Severe pain is frequently present, coupled with a few other noticeable symptoms.
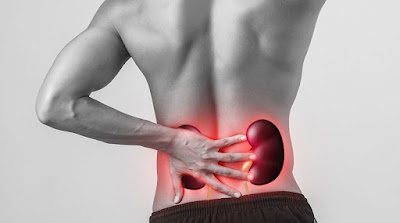
The most frequent medical problem connected to the urinary system is kidney stone formation. In the United States, there are around 600,000 instances of kidney stones every year. They are sometimes referred to as renal calculi or nephrolithiasis.
Kidney stones can occur when the body accumulates too much calcium, uric acid, oxalate, or cystine. Calcium oxalate is the most common form of kidney stone. Cystine stones are uncommon and affect persons who have a genetic condition that causes cystine from the kidneys to leak into the urine. A struvite stone is a form of kidney stone that is connected with urinary tract infections and is more common in women.
Because most kidney stones are the size of a grain of sand, they pass through the urine without creating any symptoms. However, if the stones develop to the size of a pebble or even a golf ball, they cannot pass through the urinary tract and cause pain and other symptoms.
Continue reading to learn more about the signs and symptoms of kidney stones.
Also, read about the four main types of kidney stones in this post: Different Types Of Kidney Stones: Causes and Treatments
If you have a little kidney stone, you may not notice any symptoms while it goes through your urinary tract. However, if your kidney stone is larger, you will most certainly have some symptoms.
What are the signs of kidney stones?
6 Signs and symptoms of kidney stones are listed below.
Urine with Blood
Fearsome kidney stone symptoms include bloody urine. Depending on how far down in the urinary system the stone has traveled, this symptom may not always manifest. Blood in the urine might result from a more serious or less dangerous occurrence or disease and is not always related to kidney stones. If this symptom appears, it is a good idea to consult a doctor.
A lot of urination
A kidney stone can be detected by frequent urine or at least the need to urinate, which may be accompanied by a stinging feeling when urinating. When the kidney stone travels into the lower urinary system, these symptoms are most likely to manifest. such many other symptoms, they are not exclusive to kidney stones and might indicate a different problem such a urethritis. These symptoms could last for more than 24 hours if a kidney stone is the root reason.
Vomiting and nausea
People with kidney stones frequently experience nausea and vomiting.
The kidneys and GI tract share neural connections, which results in these symptoms. Kidney stones may set off GI tract nerves, resulting in an unsettled stomach.
Your body may experience nausea and vomiting in response to severe pain.
Fever
An individual with kidney stones may occasionally experience fever and flu-like symptoms. Fever coupled with lower back and stomach aches, as well as the other symptoms described above, can indicate kidney stones, even though this is a symptom that is seldom a diagnostic indicator of the illness. This symptom is frequently brought on by kidney infection, which might develop as a result of a kidney stone.
Urine That Smells Bad
A kidney stone may be present if the urine is cloudy and smells very foul. Bacteria can accumulate behind a kidney stone that has become lodged in the urine system and result in a urinary tract infection. Approximately 8% of individuals with kidney stones also have an infection caused by the stone. Women are more prone to this. pee with an unpleasant odor and pee that is cloudier than usual are signs of a urinary tract infection.
Acute back pain
The most common symptom of kidney stones is pain. Renal colic is the medical name for this kind of discomfort. The location of the stone's lodgement affects where the pain is felt the most intensely.
It is typical to experience discomfort on one or both lower back sides, but if the stone is further down, groin pain may become more intense. Sometimes the pain radiates from the back to the stomach, creating violent spasms or a constant throbbing.
What are some of the risk factors for kidney stones?
While kidney stones can occur in anybody, several things can make you more likely to get one. While some risk factors cannot be altered, others may be managed or altered.
Kidney stones can be a greater threat to you if:
- Your diet contains a lot of sugar, salt, and/or protein
- You have polycystic kidney disease
- You consume a diet that is rich in oxalates or red meat
- You do not consume sufficient amounts of water
- You previously had kidney stones
- You have gout
- You're diabetic
Recommended post: Keto Diet: Kidney Stone Formation By Keto Diet
Summary
Kidney stones are solid deposits of salt and minerals that can leave the kidneys and spread to other areas of the urinary system.
Pain, difficulty urinating, murky or foul urine, nausea, and vomiting are all signs of stones.
Some stones will move on their own if they are small enough. Others require surgical removal or sound wave therapy to be broken up or removed.



Comments
Post a Comment
Share your views